Arup’s experience in vehicle body development and the challenges of delivering sustainable solutions ensured that the firm played a key design role in the consortium tasked with designing the SuperLIGHT-CAR.
The project’s ambitious objective was to develop technologies and concepts resulting in a 30% reduction in the body weight of a medium-sized car of the future.
Arup’s role was to ensure that key performance criteria – body stiffness, crashworthiness, fatigue and buildability – could be achieved within the constraints of mass reduction and cost.
Multi-material philosophy
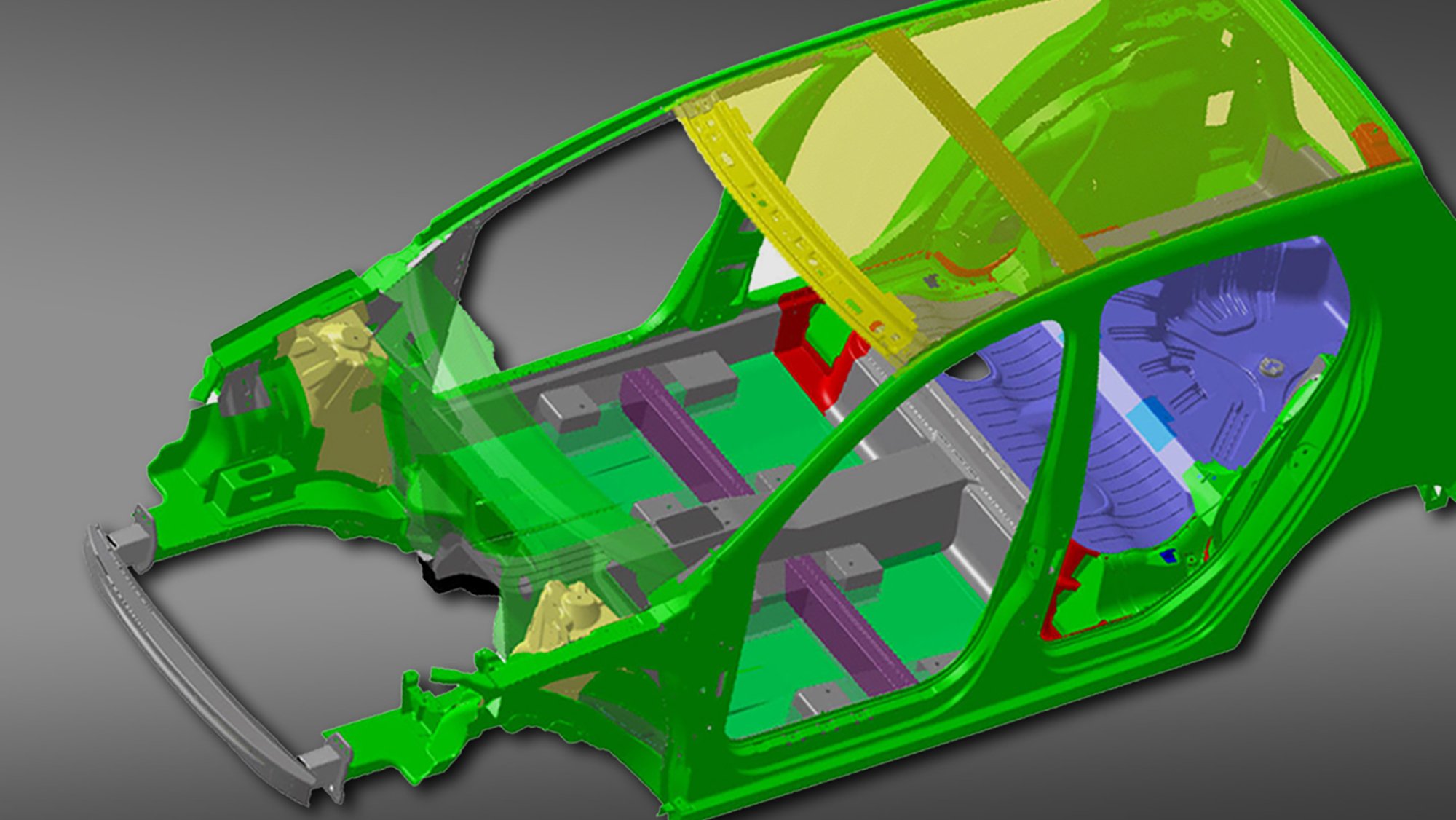
The single-material approach to traditional car body design does not necessarily offer the best solution for weight minimisation. The project therefore focused on a multi-material solution that would utilise the strengths and weaknesses of different materials.
By overcoming the challenges associated with joining materials and predicting the behaviour of the connections between them, Arup contributed to a car designed and built using a combination of steel, aluminium, magnesium and fibre-reinforced plastic.
Europe-wide collaboration
Co-funded by the European Commission, the project brought Arup into partnership with leading European car makers. Volkswagen, Fiat, Opel, Renault, Volvo, Porsche and DaimlerChrysler worked together with Arup to bring lightweight automotive technologies closer to high-volume car production.
The computer-based performance prediction capabilities of Arup’s in-house software, analysis and vehicle design specialists brought valuable insights to the design team.
Arup has many years experience of designing vehicles using these advanced methods. The dispersal of these skills in various locations across the globe helped deliver the solutions in a timely and cost-effective manner.
Finite element analysis
The finite element packages LS-DYNA and MSC Nastran were used to check and refine the design to ensure the final product met all the required performance criteria.
The design was subject to several key performance metrics: torsional and bending body modal frequencies as well as frontal, side and rear impact tests using the EuroNCAP procedure. A Volkswagen Golf 5 vehicle body was used as the reference design.
 ;
;





